Copilot for HR is quickly becoming a go-to tool for HR professionals who want to work faster and more efficiently. Built into Microsoft 365, it uses AI to automate repetitive tasks, create polished content, and analyze data — all within apps like Word, Excel, Outlook, and Teams.
As HR juggles complex workforce issues and strategic goals, Copilot helps free up time for the work that needs human judgment. Microsoft’s own HR team has seen the impact: fewer routine queries, faster data analysis, better support, and stronger candidate engagement. This article breaks down what Copilot is, how it helps HR, and how to get started.
Contents
What is Copilot?
What are the challenges of using Microsoft Copilot for HR?
6 ways you can use Copilot in HR
Pricing and licensing (July 2025)
Using Copilot in HR: Best practices
FAQ
Key takeaways
- Copilot integrates directly with Microsoft 365 apps like Word, Excel, and Teams
- It helps HR automate routine tasks (e.g., drafting, summarizing, and reporting)
- 93% of users report greater productivity, and 88% say it helps them complete tasks faster
- To unlock Copilot’s value, HR must address challenges like data privacy and user adoption
- Structured adoption is crucial — HR should pilot Copilot for high-impact workflows, training teams, and documenting internal guidelines.
What is Copilot?
Copilot is an AI assistant built into Microsoft 365 apps like Word, Excel, Outlook, and Teams. It responds to plain language prompts — such as drafting job ads, analyzing workforce data, or summarizing reports — and delivers results directly using the tools HR teams already use.
It works by combining large language models like GPT-4 with your organization’s data from Microsoft Graph (e.g., emails, documents, and calendars) while retaining existing security and permissions. For instance, you can ask Copilot to “Summarize engagement survey results by region” or “Create an onboarding plan for a new marketing hire,” and Copilot will produce clear, usable outputs in seconds.
“Copilot for HR” isn’t a separate product but a way to apply the tool to HR workflows. From speeding up recruitment to creating learning plans, it reduces admin work so teams can focus on strategy. Microsoft reports 30% to 40% faster completion of routine tasks, and a UK government trial showed an average daily time savings of 26 minutes, with over a third of users saving more than 30 minutes a day — translating to a 40% boost in productivity.
HR tip
AI in HR is most effective when you use it with a clear purpose. HR professionals who can identify where AI can make a real impact can ensure the organization is ready for adoption and equip HR teams with the right skills. Read our comprehensive AI in HR guide to learn more.
What are the challenges of using Microsoft Copilot for HR?
While Copilot for HR offers significant benefits, it also comes with challenges that HR leaders need to navigate carefully. Here are some key challenges you should be aware of:
Data privacy concerns
While Copilot only accesses information users already have permission to see via Microsoft Graph, HR must ensure sensitive employee data is properly classified and protected. As such, clear data governance policies and role-based access controls are essential to prevent accidental exposure.
Risk of outdated or biased content
Like any AI, Copilot’s responses are based on existing data and may reflect outdated information or unconscious bias. HR teams must establish review processes — particularly for content like job descriptions, performance summaries, and policy documents — to ensure current and inclusive outputs.
User resistance
Some HR professionals may be hesitant to embrace AI, either because they fear job displacement or feel unsure about the technology. Proactive HR change management, including demonstrations of how Copilot supports rather than replaces HR roles, can help build confidence and adoption.
Learning curve
Not all team members will be comfortable using generative AI tools from day one. However, providing structured training, simple usage guides, and quick-win examples can help accelerate skill-building and reduce frustration.
Integration challenges
While Copilot is built into Microsoft 365, some HR workflows rely on third-party systems like ATS or payroll software, which means HR teams may need to invest in process alignment or API integrations to make Copilot truly effective.
Cost considerations
Copilot is a premium, per-user add-on for Microsoft 365, so HR teams must weigh its potential productivity gains against the additional licensing fees they must pay. This applies especially to large organizations, which may need to purchase hundreds or thousands of licenses.
Over-reliance on automation
Without sufficient human oversight, Copilot could unintentionally undermine HR’s strategic and relational role, especially in areas requiring empathy and nuance, like employee relations or performance discussions. As an HR leader, you must clearly establish boundaries for where human judgment remains essential.
Master generative AI to boost your HR function
To boost all aspects of your HR function using generative AI (Gen AI), learn to align the right tool with your existing tech stack, and train your team on effective AI use.
✅ Master Gen AI prompt techniques, apply them correctly and effectively
✅ Identify opportunities to integrate Gen AI into HR tasks and workflows
✅ Explore HR-specific use cases within different Gen AI applications
✅ Choose the right Gen AI solution to solve your HR challenges.
Learn at your own pace with the online Artificial Intelligence for HR Certificate Program.
6 ways you can use Copilot in HR
By automating repetitive tasks and pulling together insights from multiple data sources, Copilot lets HR spend less time on manual processes and more time on strategic planning and activities. Below are the different aspects of HR where Copilot can be useful:
1. Recruitment and hiring support
Copilot drafts job postings, offer letters, and rejection letters in Word, generates interview questions, and even compares candidate résumés to highlight key differences and similarities. This speeds up screening and documentation, so HR can focus on decision-making rather than admin work.
Copilot in action
- After meeting with a hiring manager, open Word and prompt Copilot: “Draft a job description for a Software Engineer role based on these meeting notes. Include skills, responsibilities, benefits, and our company tone.”
- Once applications arrive, paste shortlisted CVs into Word and ask: “Compare these five candidates, summarizing qualifications, certifications, and leadership experience in a table.”
- In Teams, use Copilot to “Draft 10 interview questions for this role based on the job description.”
- Once a candidate is chosen, use Word to prompt: “Write an offer letter for Jane Smith for the Software Engineer role, including salary, bonus, holidays, and our benefits package.”
- For other candidates, ask: “Draft a professional but empathetic rejection email to John Doe, thanking him for applying and encouraging him to apply for future roles.”
2. Onboarding and employee experience
Copilot automates the creation of onboarding documents, personalized welcome plans, and knowledge-based content for employees. Microsoft’s HR department even uses custom Copilot agents (via Copilot Studio) to power self-service “Ask HR” bots, reducing calls to HR reps and enabling faster employee support.
Copilot in action
- In Word, prompt Copilot: “Create a two-week onboarding plan for a new Sales Associate. Include training milestones, introductions, and links to IT and HR resources. Use our onboarding handbook as a reference.”
- Personalize the plan by asking Copilot to “Adapt this plan for the Marketing team’s new hires, focusing on collaboration tools and campaign processes.”
- In Copilot Studio, build a self-service “Ask HR” bot that can answer FAQs on benefits, IT setup, and payroll, drawing from internal policy documents (Microsoft uses this to reduce HR call volumes).
- Test the bot by prompting sample employee questions and refining answers, so HR reps handle fewer repetitive queries and focus on culture-building.
3. Employee engagement and policy updates
HR teams use Copilot to draft employee surveys, summarize engagement data, and identify trends in your company’s Employee Net Promoter Scores (eNPS). It can also review regulatory updates (e.g., working time directives), compare them to internal policies, and draft clear, scenario-based knowledge articles to simplify compliance for staff.
Copilot in action
- In Microsoft Forms, use Copilot to “Draft a 5-question pulse survey to identify drivers of disengagement, focusing on workload balance, communication, and recognition.”
- Collect responses, then in Excel, ask Copilot: “Segment eNPS scores by department and tenure, and highlight three engagement drivers with the lowest ratings.”
- In Word, prompt Copilot: “Draft a one-page summary of these insights with recommended next steps for managers.”
- For policy updates (e.g., Working Time Directive), ask Copilot: “Compare our internal working time policy to these new E.U. guidelines. Summarize differences, draft three scenario-based knowledge articles for employees, and link to source documents.”
- Upload the articles to the “Ask HR” bot so employees can access updates without waiting for HR assistance.
4. Data analysis and reporting
Copilot, layered over Excel and Power BI, helps HR analyze large data sets (e.g., engagement scores by demographic or region), identify trends, and produce summaries or visualizations for leadership presentations. It can also generate PowerPoint decks from Word or data outputs, automatically structuring the story with headlines and visuals.
Copilot in action
- In Excel, load workforce data (demographics, turnover, engagement). Prompt Copilot: “Summarize these metrics by department and region. Identify 3 key trends and anomalies that leadership needs to see.”
- Once insights are ready, open PowerPoint and ask: “Create a 10-slide presentation from these findings with clear headlines, charts, and speaker notes. Use our corporate template.”
- Review Copilot’s draft slides (as shown in the transcript, Copilot can create 20+ slides in under a minute) and refine content. This ensures accuracy before presenting to leadership.
5. Meeting productivity and action tracking
Using Copilot in Teams, HR can capture and summarize meeting notes, pull out action items by speaker, and distribute summaries without needing a dedicated note-taker.
Copilot in action
- Enable Copilot in Teams for an HRIS implementation meeting.
- During the session, let Copilot transcribe and tag speakers automatically.
- After the meeting, ask Copilot: “Summarize this meeting by theme. List action items with owners and deadlines. Draft a follow-up email to all attendees summarizing decisions.”
- Review Copilot’s output, tweak it as needed, and then send it. This saves the team from manual note-taking and follow-up.
6. Case resolution in Outlook and CRM
Copilot assists HR support teams by checking for similar cases, drafting professional email responses to managers or employees, and linking interactions back to HR systems with one click. This accelerates response times while maintaining consistency.
Copilot in action
- If, for instance, you receive a manager’s email about flexible work rules, ask Copilot in Outlook: “Check for similar active cases and draft a professional response, referencing our policy and U.S. employment law.”
- Review Copilot’s draft, adjust tone or specifics, then send it.
- With one click, use Copilot to attach the email and case notes to the HR CRM record, logging the interaction automatically (as Microsoft HR’s service team does).
Pricing and licensing (July 2025)
Copilot for Microsoft 365 is a premium add-on and is not included in standard Microsoft 365 subscriptions. However, you can purchase Microsoft Copilot licenses online through Cloud Solution Providers (CSPs) or Microsoft’s direct channels.
- Annual billing: US$30 per user per month.
- Monthly billing: Carries a 5% premium, meaning approximately US$31.50 per user per month, but you remain committed to a full year of service.
Licensing requirements
Qualifying Microsoft 365 License: To purchase Copilot, you must already have an eligible Microsoft 365 license. These include:
- Microsoft 365 Business Standard
- Microsoft 365 Business Premium
- Microsoft 365 E3 or E5
- Office 365 E3/E5
- Other enterprise plans such as F1/F3, A3/A5 may also qualify, depending on your organization’s agreement.
- There is no minimum seat count, which means that as of 2025, you can buy Copilot for a single user. This is ideal for pilot programs or small businesses.

Using Copilot in HR: Best practices
From writing crystal-clear instructions to managing data privacy and keeping humans at the center of decisions, these best practices will help your team use Copilot effectively and responsibly:
Offer clear, context-rich prompts
Copilot works best with specific instructions. Instead of “Summarize this policy”, for instance, use: “Summarize this flexible work policy into three bullet points for employee training slides, using plain language for non-legal audiences.” Detailed prompts improve tone, format, and context, reducing edits.
Always review AI outputs
Copilot is a helper, not an autopilot, so its AI content can be outdated, biased, or inaccurate. Always review outputs — especially for sensitive messages, job ads, or engagement materials — to ensure accuracy, tone, and compliance.
Train your team on privacy and responsible AI use
Copilot uses Microsoft Graph data (documents, emails, chats), so HR must understand permissions and privacy settings. To prevent data exposure, provide training on sensitivity labels and when not to use Copilot, such as for highly confidential cases.
Focus on high-value use cases
Deploy Copilot where it delivers the most impact:
- Word: Job descriptions, offer letters, rejection emails, onboarding guides.
- Excel and Power BI: Engagement, turnover, workforce analysis.
- Teams: Meeting summaries, action items, follow-ups.
- Forms: Employee surveys and feedback collection.
You should also map time-heavy workflows and start with those for quick wins.
Document internal guidelines
Create a playbook with sample HR prompts, review and approval processes, and escalation checklists for legal, disciplinary, or regulatory matters. Sharing this guidance company-wide will then ensure consistent quality and adoption.
Provide ongoing training
Go beyond onboarding, and encourage teams to use courses like AIHR’s Gen AI Prompt Design for HR mini course or Microsoft’s Copilot learning paths. Host monthly “prompt labs”, where staff can share tips and use cases with one another.
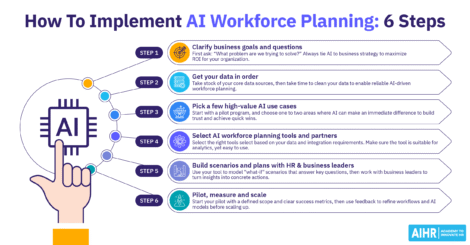
Pilot, measure, and scale
Start small — target one or two workflows, such as recruitment or engagement reporting. Before expanding the use of Copilot at your organization, track results, including time saved, faster case resolution, or improved eNPS.
Keep humans at the center
Automation is valuable, but sensitive decisions and employee interactions need a human touch. Balance self-service tools with access to HR professionals to maintain trust and judgment quality.
Next steps
If you’re ready to incorporate Copilot in HR, start by identifying one or two time-consuming workflows (e.g., recruitment documentation or engagement reporting), and use Copilot there first. Measure the time saved and how employee and manager experiences may have improved. Once you see the impact, you can expand its use across other HR functions.
To boost adoption and confidence, consider upskilling your team with programs like AIHR’s Using Gen AI in HR online course or Microsoft’s Copilot learning paths. These small, practical steps will help you integrate AI responsibly and ensure your team is using Copilot to drive real, measurable results, reinforcing HR’s position as a strategic business partner.
FAQ
Copilot is embedded in Microsoft 365 tools like Word, Excel, Teams, and Outlook, helping HR teams work faster and smarter. It automates repetitive tasks like drafting job descriptions, summarizing engagement surveys, creating reports, and even generating presentations, so HR can focus on strategy, people, and culture rather than admin.
Recruiters use Copilot to speed up the hiring process by drafting job ads, interview questions, offer letters, and candidate comparisons. By prompting Copilot with specific instructions (e.g., “summarize these five CVs into a comparison table”), recruiters save time on documentation and screening, and can spend more time engaging suitable candidates.
Yes, Copilot is built with Microsoft’s enterprise-grade security. It only accesses data users already have permission to see, using existing Microsoft Graph permissions. To keep sensitive employee information secure, companies should configure data classifications, apply role-based access controls, and train teams on responsible use.