Generative AI is becoming part of everyday HR, with around 25% of organizations already using it to support key processes. According to SHRM’s Talent Trends report, 75% of HR professionals believe AI will increase the value of human judgment over the next five years. This shift is moving HR from task execution to roles focused on culture, empathy, and inclusive leadership.
Today, HR leaders are applying AI across nearly every function. From recruiting and onboarding to performance, learning and development (L&D), and employee engagement, companies are using AI to personalize training, assess skills gaps, monitor sentiment, and automate routine tasks.
Still, adoption isn’t without challenges. Nearly half of AI projects launched this year were abandoned due to unrealistic expectations, poor workflow fit, or weak ethical foundations. For AI to truly work in HR, innovation must be grounded in strong governance with transparency, fairness, and human oversight.
This article looks at how generative and agentic AI are reshaping HR. We’ll cover common roadblocks, ethical concerns, real-life examples, and practical steps for using AI in your HR strategy, from pilot use cases to setting up a governance framework that combines AI with human expertise.
Looking to get started? Download our ChatGPT Prompts for HR Guide — it’s packed with ready-to-use prompts for hiring, development, feedback, analytics, and more to help your team use AI effectively while keeping people front and center.
Contents
What is generative AI in HR?
How generative AI impacts HR
8 generative AI use cases in HR
Top generative AI tools for HR
5 generative AI in HR examples
How to start using generative AI in HR
FAQ
What is generative AI in HR?
First, let’s explore generative AI and what it means for HR specifically.
What is generative AI?
Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence designed to create new content such as text, code, images, or audio. It does this by learning patterns from large datasets and producing outputs that mimic human-like creativity.
While traditional AI focuses on analyzing and processing existing data to make predictions or decisions, generative AI goes a step further. It generates original content by recognizing and replicating patterns and structures found in vast amounts of training data. This data can include anything from written text and images to video and music.
What is generative AI in HR?
Generative AI’s application can have significant implications for four main areas of HR:
- Content: HR professionals can use generative AI tools to boost efficiency and value in various stages of the employee life cycle. This includes creating job descriptions tailored to skill profiles, writing personalized candidate emails, drafting policies, and generating training materials.
- Data: These tools can analyze and summarize large datasets, helping HR teams quickly extract insights. For example, generative AI can assist in reviewing performance data, compensation trends, or survey results.
- Communication: Generative AI chatbots enhance employee engagement by making HR support more accessible. They can answer policy questions, suggest learning content based on skill gaps, and guide employees through onboarding or benefits processes—making interactions more personalized and timely.
- Coding: While not every HR professional codes, generative AI can compile and analyze complex data for workforce planning. It can help forecast attrition risk, identify high-potential employees, and highlight future skills gaps.
How does generative AI work?
Generative AI relies on neural networks, which are systems inspired by how the human brain processes information. These networks are trained on large datasets to recognize patterns and then use those patterns to produce new content.
For example, a model trained on thousands of images can generate new images that resemble the originals. Similarly, a text-based model can write new paragraphs in a style and tone similar to the material it was trained on.
Master the use of AI to streamline your HR processes
As AI rapidly transforms the world of work, learning how to apply it effectively can help make your HR function faster, smarter, and more impactful.
✅ Learn how to use generative AI in HR to produce high-quality work
✅ Craft the right prompts to get the best results from AI tools
✅ Build hands-on skills with the most widely used generative AI platforms
✅ Identify opportunities to integrate Gen AI into HR tasks and workflows
🎓 Future-proof your HR career with a flexible, online Artificial Intelligence for HR Certificate Program.
How generative AI impacts HR
Generative AI has shifted from a promising technology to a transformational force in HR. According to McKinsey’s State of AI report, more than 78% of organizations now use generative AI in at least one function, and many are redesigning workflows and placing AI governance under the direct oversight of CEOs or boards to ensure alignment with business priorities.
In HR, the biggest gains show up in talent acquisition, performance management, learning, and workforce planning. AI helps automate routine work, personalize employee experiences, and deliver data-driven insights faster, freeing up HR teams to focus on human interaction and strategy.
This shift is also changing the skills organizations prioritize. As routine tasks become automated, demand is rising for cognitive and social skills, such as problem-solving, critical thinking, collaboration, and empathy. Organizations are responding by investing in upskilling and repositioning employees into AI-augmented roles.
However, adoption is not without hurdles. Only 1% of organizations consider their generative AI strategy mature, and many report limited impact due to scattered pilot programs and weak coordination. Bias remains a concern, particularly in recruitment, where some models have been shown to favor male candidates for higher-paying roles.
Trust and transparency are critical. Employees need clear communication about how AI is used, how it supports rather than replaces their roles, and what reskilling options are available. Without this foundation, even well-designed AI initiatives can fall flat.
For a closer look at how these ideas play out in practice, let’s explore eight high-impact generative AI use cases across HR.
8 generative AI use cases in HR
Generative AI is becoming a valuable tool across HR, helping teams work more efficiently and focus on higher-impact activities. Here are eight practical ways it’s being used across the employee life cycle.
1. Recruitment and hiring
Generative AI tools like ChatGPT can help create clear, compelling job postings and generate customizable screening questions tailored to specific roles and candidate profiles. This leads to more targeted and effective interview processes.
HR and talent acquisition professionals can also use generative AI to draft various types of emails in the recruitment process, such as outreach emails and rejection letters.
Some talent intelligence platforms now integrate generative AI to simplify candidate searches. Instead of writing complex Boolean strings, recruiters can input natural language questions and receive refined results. These platforms can also analyze candidate profiles in relation to job requirements, improving match quality.
2. Onboarding
AI-powered chatbots can serve as virtual onboarding assistants, offering real-time support to new hires. They can answer common questions about company policies, compensation and benefits, time-off procedures, and more. This improves the onboarding experience and helps new employees settle in more quickly.
3. Training and development
Generative AI can support employee growth by recommending personalized learning paths based on skill gaps, performance data, and career aspirations.
AI-based coaching is also growing in popularity. These platforms mimic one-on-one coaching by providing real-time feedback, answering employee questions, and offering tailored insights.
AI can also keep training content up to date by adapting materials to meet changing industry standards. In addition, generative AI can create dynamic training simulations that respond to user input, enhancing experiential learning and decision-making skills.
4. Employee engagement
As an HR professional, you can use generative AI to brainstorm employee engagement survey questions that will allow you to gather actionable insights into how you can improve workplace satisfaction, enhance productivity, and address specific areas of concern within your organization.
AI chatbots can also support engagement by assisting not just new hires, but all employees. They can handle routine employee queries regarding essential company information (such as benefits and policies) and enable HR to offer more intuitive self-service options. This gives HR professionals more time to spend on more valuable face-to-face interactions.
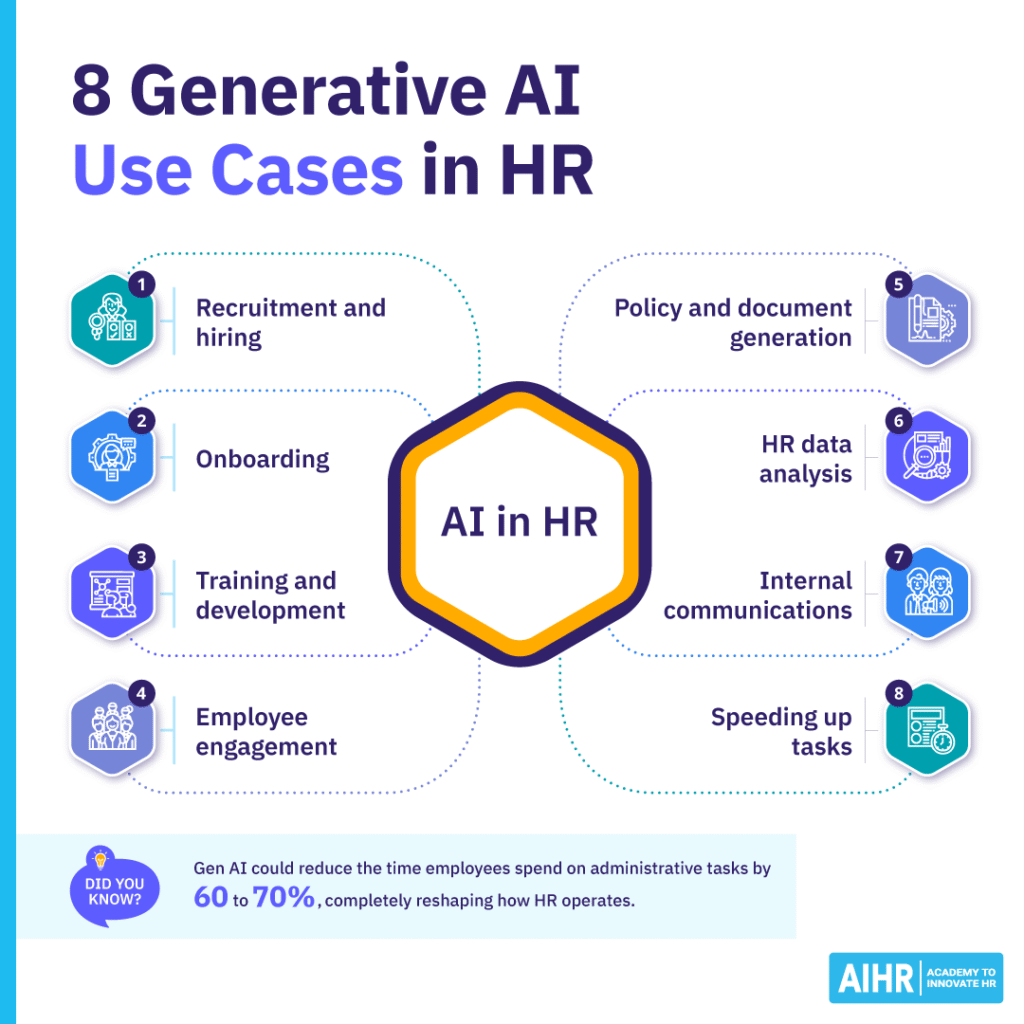
5. Policy and document generation
Generative AI is highly effective in creating and updating HR documents. It can draft policies, agreements, and contracts based on existing guidelines, streamlining the writing and research process.
It also helps complete forms and templates more efficiently, reducing the administrative burden on HR professionals and minimizing errors in routine paperwork.
6. HR data analysis
Generative AI can process and summarize large HR datasets, uncovering trends and anomalies that might otherwise go unnoticed. It can also generate visually engaging reports and data visualizations to simplify complex findings.
For example, HR teams can use AI to identify patterns in anonymized salary data, attendance records, or performance reviews, surfacing issues such as employee dissatisfaction or managerial challenges. AI can even assist in writing scripts for deeper, more customized data analysis.
7. Internal communications
Generative AI allows you to quickly generate content tailored to the organization’s and its employees’ needs. This includes determining a voice and tone that aligns with company values, personalizing messages to resonate with the individual, and using inclusive language. This helps HR ensure all communications across the business are consistent in tone, inclusivity, and engagement.
Gen AI can also customize messages based on factors like role, interests, location, and professional development stages. Whether you’re engaging with candidates or existing employees, it can help ensure every aspect of your communication is deliberate and effective.
8. Speeding up tasks
If appropriately used, generative AI enables HR professionals to complete repetitive tasks faster, freeing up a significant amount of time. This allows them to focus on more strategic and value-added activities such as employee development, talent management, and organizational planning. Not only does this help HR teams feel more valued and purposeful, but it also makes them more integral to business growth.
HR tip
If you want to boost your productivity and stay ahead with tools like ChatGPT, consider joining a course or workshop that focuses on practical, HR-specific applications of generative AI.
AIHR’s ChatGPT for HR course is a great example. It’s fully online, self-paced, and designed to help you use AI effectively in areas like recruitment, communication, and learning—no technical background required.
Top generative AI tools for HR
HR software providers are quickly adding generative AI features to their platforms, but not all tools serve the same needs. The right choice depends on your team’s goals, the size and maturity of your organization, and how AI currently fits into your HR processes.
When choosing generative AI tools, it’s important to consider the difference between enterprise-wide platforms and specialized point solutions.
- Enterprise-grade platforms: Tools like Workday, SAP SuccessFactors, and Oracle HCM offer integrated AI across the full HR lifecycle. These platforms support functions such as recruitment, onboarding, performance, learning, and workforce planning. They are designed for large organizations that need consistent data structures, built-in governance, and scalability. However, they usually involve a higher upfront investment, longer implementation timelines, and significant change management.
- Point solutions: Tools such as Findem for talent acquisition or Diversio for DEIB analytics focus on specific HR areas and are faster to implement. These solutions are a good fit for organizations with targeted priorities or those just beginning to explore AI in HR. While some integration may be needed, they offer flexibility and often deliver faster results. Many teams use point tools to test and demonstrate value before expanding AI across the organization.
Below is a breakdown of top tools grouped by purpose and scope.
Entry-level tools
Great for experimentation and small teams
General-purpose HR tasks
Versatile, cost-effective, useful for content, communication, job descriptions, and prompt engineering.
Employee self-service and automation
Automates common employee queries and supports onboarding, payroll, and benefits through conversational AI.
Total rewards communication
Offers a built-in AI assistant (“Beni”) that provides 24/7 personalized employee support and integrates with HR systems.
These tools are user-friendly, require minimal technical onboarding, and help HR teams understand GenAI’s potential before scaling up.
Enterprise-grade platforms
Integrated AI for large-scale HR operations
Full-suite HCM
AI is embedded across recruiting, performance, and workforce planning. Strong fit for large enterprises.
Core HR and talent management
Supports smart recommendations, learning paths, and bias reduction. Integrates well with SAP systems.
End-to-end HR processes
Delivers AI-driven insights across the talent lifecycle, including adaptive workforce planning.
These tools are easy to use, require minimal technical setup, and help HR teams explore AI’s potential before scaling up.
Specialist tools
Deep functionality in specific domains
Talent sourcing and intelligence
Uses AI and attribute-based filters to improve candidate diversity and quality.
DEIB analytics
Uses AI to uncover bias patterns and recommend targeted inclusivity actions.
Talent intelligence and upskilling
Supports predictive hiring, skills matching, and career pathing. Great for workforce planning and reskilling.
These tools are best suited for organizations focused on specific HR priorities like DEIB, upskilling, or workforce intelligence, and that already have a foundational HR system in place.
AI-embedded workflow tools
Helpful tools outside the core HR tech stack
Internal knowledge and comms
Assists with drafting HR documents, policies, onboarding materials, and meeting notes.
Workplace productivity
Embedded in Microsoft 365, supports HR teams with writing, summarising, data analysis, and goal tracking.
Communication and content creation
Improves clarity, tone, and inclusiveness in HR emails, policies, and feedback.
While not explicitly built for HR, these tools offer meaningful productivity gains when integrated into daily workflows. They are especially helpful in communication, learning, and operational tasks.
5 generative AI in HR examples
Let’s look at how companies are successfully applying generative AI in HR.
Example 1: Lattice
In early 2025, Lattice, a people success platform, rolled out an AI-powered HR agent to improve internal support and allow HR teams to focus on more strategic work. The agent handles routine employee questions about policies, payroll, benefits, and more by pulling information from internal documents and systems to deliver quick, context-aware answers.
It also goes beyond basic support by detecting disengagement signals, offering coaching prompts to managers, and suggesting personalized development opportunities for employees. The platform enables HR teams to create their own AI agents for tasks like onboarding, IT support, and workforce planning using no-code templates, making the technology easy to scale without relying heavily on engineering.
Since launch, clients like Figma and Red Door Interactive have reported faster performance review cycles and higher engagement. Lattice has also seen a 250% increase in HRIS adoption, driven by strong interest in the new AI features. Throughout the rollout, the company has emphasized transparency and human oversight, avoiding the framing of agents as “AI employees”.
Example 2: Yahoo Japan
Yahoo Japan now requires all 11,000 employees to use generative AI in their daily workflows, with the ambitious goal of doubling overall productivity by 2028. The mandate covers tasks that reportedly account for about 30% of employees’ work time, including research, document creation, meeting agenda and minute preparation, expense claims, proofreading, and competitive analysis.
The company’s internal tool, SeekAI, powers much of this effort. Initially deployed for expense processing and prompt-template-based data queries, SeekAI is now being rolled out more broadly to handle routine office work like summarising meetings, drafting documents, crafting agendas, and proofreading reports, helping employees shift their focus toward higher‑value creative and strategic tasks.
Example 3: Moderna
Moderna has taken a bold approach to generative AI by partnering with OpenAI and rolling out ChatGPT Enterprise across the company. By mid-2025, the biotech firm had developed over 3,000 custom GPTs to support a wide range of functions, including HR tasks like onboarding, benefits inquiries, and performance management.
A central tool called “Ask HR” serves as the front end, directing employee questions to specialized GPTs focused on areas such as career development, equity, and total rewards. These HR-specific GPTs now handle tasks that were once managed by junior analysts, such as summarizing self-reviews, answering benefits eligibility questions, and supporting job leveling.
By routing questions through multiple targeted GPTs, the system delivers faster, more accurate responses while reducing internal ticket volume. The data from recurring queries also helps HR teams identify trends and fine-tune policies and engagement efforts.
Example 4: RingCentral
RingCentral, a cloud comms and collaboration software business, knew its talent search wasn’t fast enough to meet recruitment targets or DEI goals. Enter Findem’s talent search solution: a generative AI approach that delivers detailed talent insights and trends by combining external and internal data and automating candidate matching and outreach.
The advanced talent data cloud with attribute-based search enables RingCentral to find and hire the right talent and create highly targeted and diverse talent pools. They’re also able to gain insight into what could motivate each candidate to consider taking the job, then create targeted outreach campaigns based on their findings. RingCentral increased its pipeline by 40%, its pipeline quality by 22%, and increased interest in its vacancies from underrepresented groups by 40%.
Example 5: Manipal Health Enterprises
Manipal Health Enterprises wanted a solution that could provide 24/7 support to nurses, doctors, and other employees for all their HR queries. Using Leena, MiPAL was born — a virtual assistant that automatically answers all queries relating to payroll, taxes, leave management, benefits, and more.
This has saved the HR team over 60,000 hours in time manually replying to repetitive questions, reduced the average response time for employees to 24 hours, and reduced the annual new hire attrition rate by up to 5%.
How to start using generative AI in HR
Here are some best practices to familiarize yourself with before you begin using generative AI in your HR operations:
Step 1: Start small and experiment
ChatGPT is a great free tool to begin exploring generative AI. Try using it to brainstorm employee survey or interview questions, draft emails to candidates, or revise job descriptions. These small, low-risk tasks are a solid way to test the waters and build familiarity before committing to a larger investment.
Step 2: Learn how to prompt effectively
Writing a clear prompt is key to getting useful outputs. Focus on three elements:
- Objective: This is the purpose of the prompt. It clarifies what you want to achieve with your query.
- Context: Any relevant background information that provides a framework for your query. This might involve specifying the topic or including necessary details that can guide the response.
- Format: Specifying any particular formatting requirements (e.g., list, summary, paragraph).
An example of a prompt would be “Draft a job description for the role of HR Administrator at Mastercard, covering responsibilities and what we offer.” Try varying your prompts to see which phrasing yields the best results.
Step 3: Evaluate and refine based on the AI outputs
It’s important to remember that generative AI is constantly evolving. Review the AI-generated responses, gain insights into the effectiveness of your queries, and identify areas for improvement in prompt crafting to get more accurate and relevant information. Always apply your professional judgment and industry knowledge to assess quality and correctness.
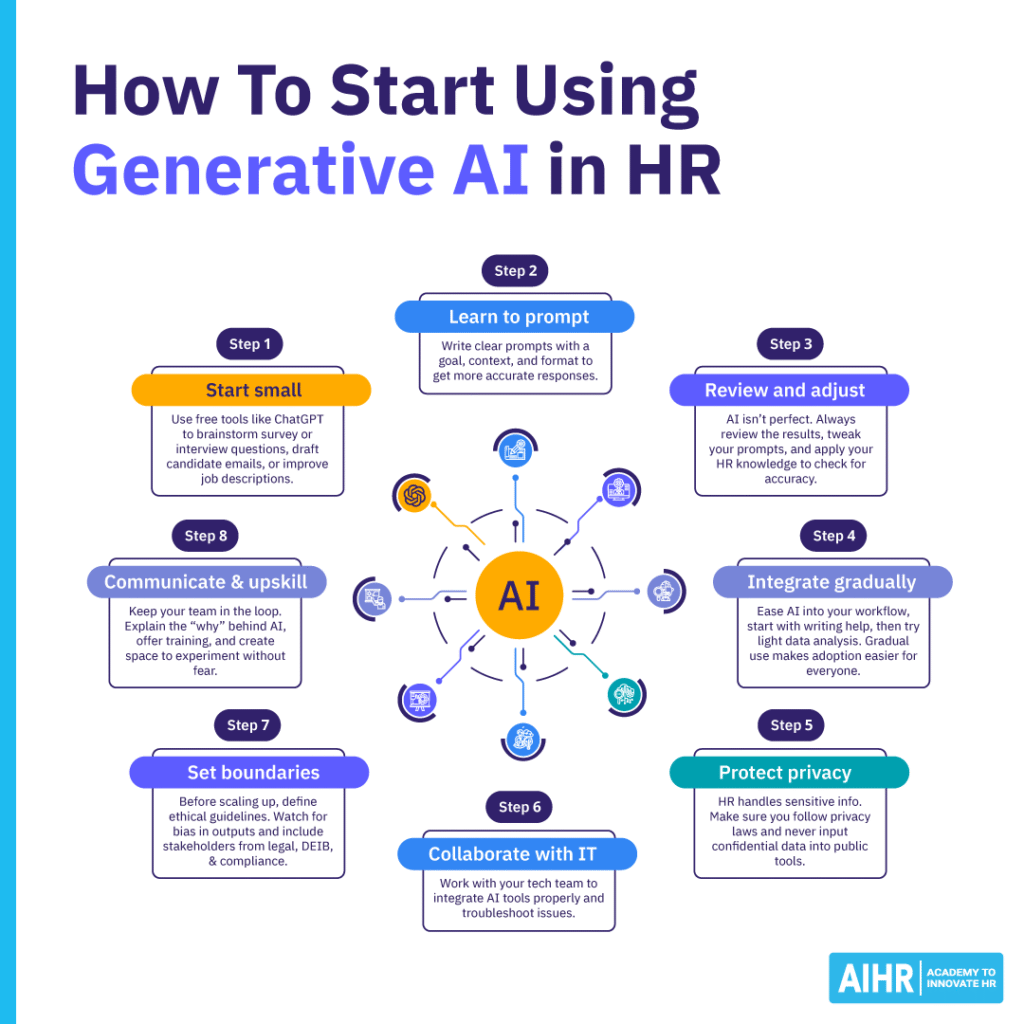
Step 4: Integrate AI gradually
Don’t try to overhaul your workflow overnight. Start by using AI for low-stakes tasks like drafting policy documents. The following week, try it for basic data summaries. A gradual rollout helps your team adapt at a manageable pace.
Step 5: Keep data privacy top of mind
HR professionals work with sensitive information, so it’s essential to protect employee data when using generative AI. Comply with data protection regulations and avoid feeding confidential details into unsecured systems.
As GenAI becomes more widely used within your HR department and the organization, consider developing a generative AI policy to guide how you work with technology.
Step 6: Collaborate with IT
Partner with your IT team to understand how generative AI tools fit into your existing systems. Not only will this help you integrate them properly into your existing HR software and systems, but it will also minimize technical issues and facilitate smooth operations.
Step 7: Prioritize governance and bias mitigation
Before scaling up, put safeguards in place. This includes establishing governance frameworks to ensure transparency, fairness, and ethical AI use. Generative AI can unintentionally reflect or amplify bias, especially in areas like hiring and performance reviews. Regular audits, documented decision processes, and involvement from legal, compliance, and DEIB stakeholders are essential.
Step 8: Communicate and upskill internally
Generative AI adoption can create anxiety around job security, fairness, or surveillance. To avoid resistance, communicate clearly with your HR team and broader workforce about how AI will be used, why it’s being implemented, and what safeguards are in place. It’s also essential to provide opportunities for experimentation and upskilling so employees feel empowered rather than replaced.
Next steps
Generative AI marks a foundational shift in how HR operates and delivers value. By embracing AI strategically and responsibly, HR professionals can free themselves from administrative overload and step into more impactful roles as people leaders, culture architects, and strategic partners. The key is to start small, learn quickly, and scale with intention. Whether you’re drafting smarter job ads, automating onboarding, or building personalized L&D journeys, now is the time to experiment.
FAQ
One practical example is using ChatGPT to draft personalized job descriptions based on specific skills and team needs. Instead of starting from scratch, HR professionals can input key role details and generate descriptions that align with the company tone, DEI language, and candidate expectations. Some organizations go further by using AI-powered tools to screen résumés, generate interview questions, and provide real-time feedback to hiring managers. This speeds up hiring while keeping the process people-focused.
Generative AI is transforming HR by automating routine tasks and enabling a more strategic, data-informed approach to people management. It helps HR professionals deliver personalized experiences across the employee life cycle, from recruitment and onboarding to development and performance. It also improves decision-making, communication, and operational efficiency. At the same time, it introduces new responsibilities, such as managing ethical risks, mitigating bias, and ensuring transparency. When adopted thoughtfully, it allows HR to shift from task execution to strategic leadership.